How Delete All Partitions and Format It Again in Linux in Command
Your hard bulldoze is commonly partitioned into logical volumes called partitions. Partitions help you organize your data and hence allow you to easily remember your saved files and folders. You can hands create partitions to make space for data storage too as delete them.
There are 2 means you can delete a partition in Linux:
- Using the fdisk command-line utility
- Using the Gparted GUI tool
Delete a Partition Using the fdisk Command-line Tool
The fdisk control-line utility is a tool that ships with every Linux distribution and comes in handy when yous desire to create or delete hard disk drive partitions.
Usually, partitions take naming conventions, as shown below:
For IDE drives: /dev/hdx e.g /dev/hda , /dev/hdb, /dev/hdc
For ISCI disks: /dev/sdx e.thou /dev/sda, /dev/sdb, /dev/sdc
Before deleting a sectionalisation, it is imperative that you back up all the files and directories since they are going to be wiped out.
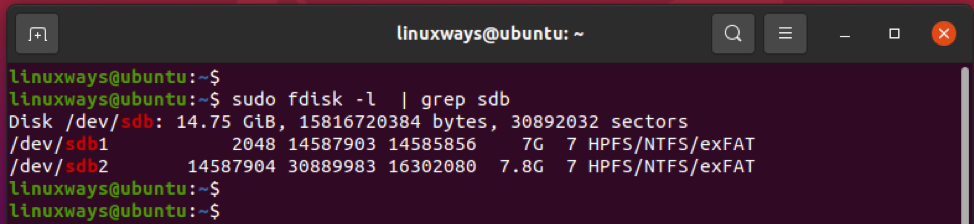
In my system, I accept fastened a removable drive, /dev/sdb, with 2 partitions. To display the partitions, I volition execute the fdisk control equally shown. If you are using a regular user, ensure to use the sudo command since fdisk requires elevated privileges.
$ sudo fdisk -l | grep sdb
Alternatively, you can use the lsblk control to go a improve visual every bit follows:

The drive has 2 partitions: /dev/sdb1 and /dev/sdb2. I'g going to delete the second partition, which is /dev/sdb2.
To get started, invoke the fdisk command-line tool:
Side by side, you volition be prompted to enter a command to proceed. Type 'P' to impress the existing partitions on the drive.
Command (m for help): p
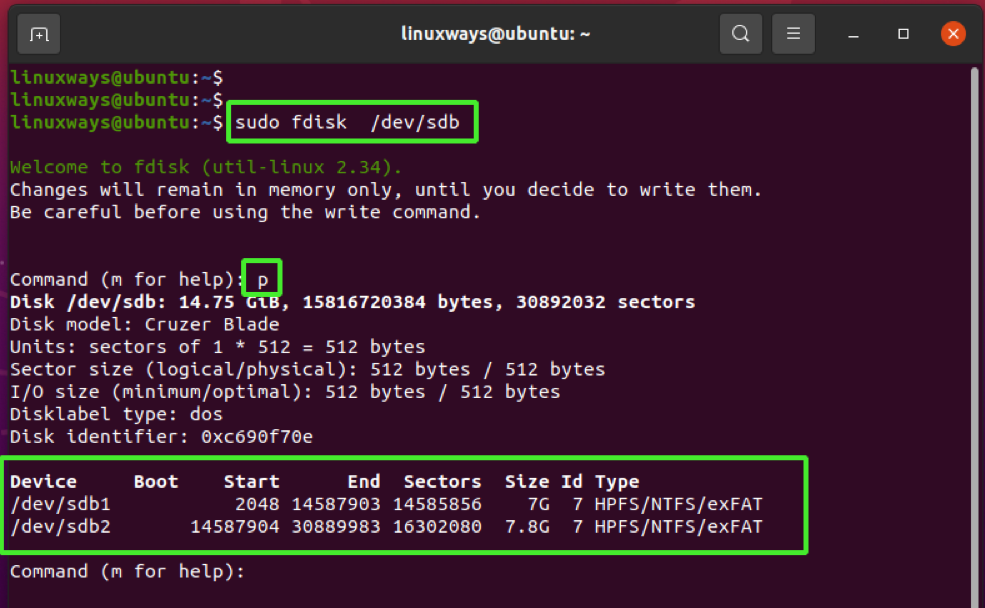
To remove the partition, type the letter 'd' which stands for delete and
Press "ENTER".
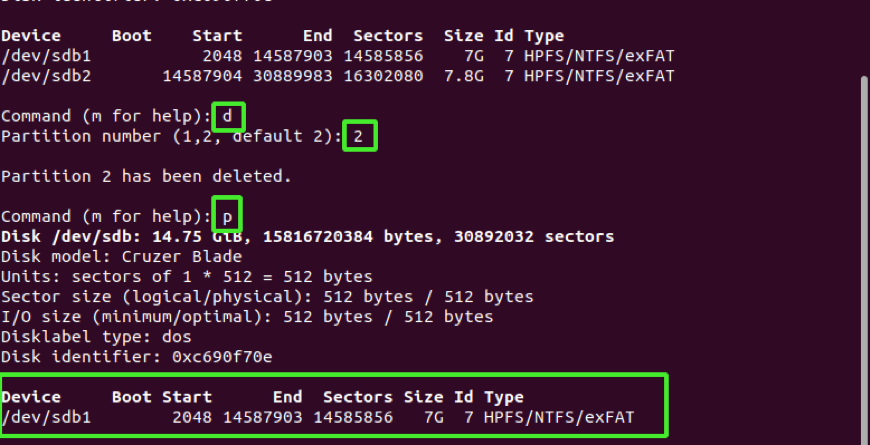
Command (1000 for aid): d
Thereafter, provide the segmentation number. In my case, I volition type ii and printing "ENTER" since this is the partition that I intend to delete.
Sectionalization number (i, two, default 2): 2
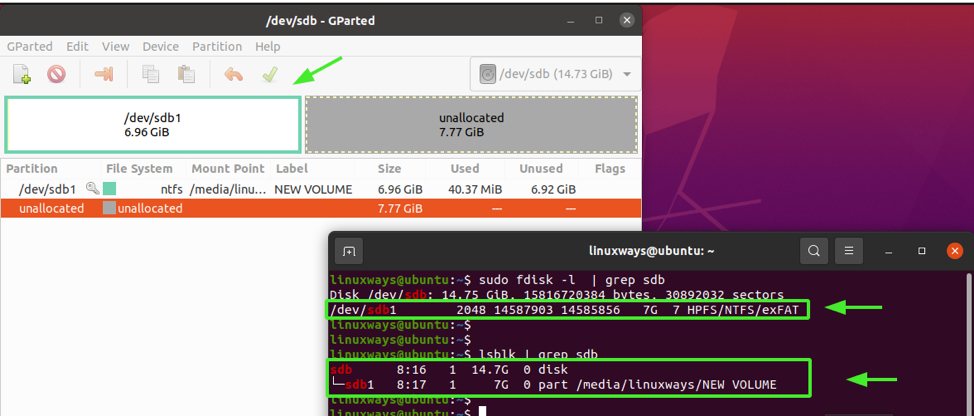
Y'all will be notified that the partition has been removed or deleted. You can cross-bank check past printing out the partitions again by typing the p command.
At the bottom of the snippet below, only /dev/sdb1 is listed.
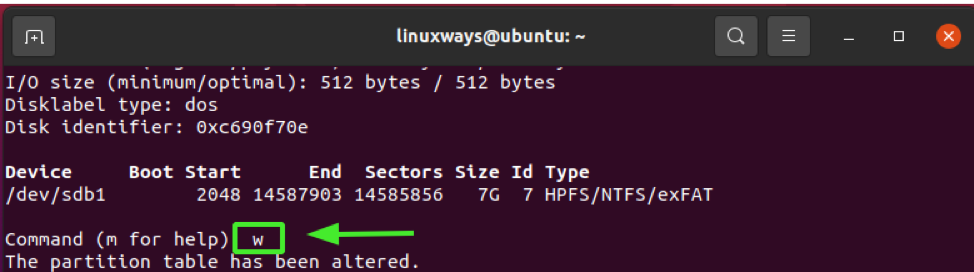
To save changes to the disk, type w for write and press "q" to quit the fdisk shell.
Equally before, confirm the existing partitions using the fdisk tool.
$ sudo fdisk -l | grep sdb

Delete a Partition Using the GParted Tool
Gparted is a powerful graphical tool that allows you to view, resize, create and delete your partitions. It is open-source and absolutely gratuitous and can be installed as follows:
For Debian/Ubuntu Distributions
For Debian/Ubuntu distros, run the command below to install Gparted:
$ sudo apt install gparted
For CentOs
For CentOS-based systems, beginning, install EPEL. Then install Gparted using the yum package director:
$ sudo yum install epel-release
$ sudo yum install gparted
For Curvation
For Arch and Arch-based distros, invoke:
To launch Gparted, run the following command on the concluding:
Also, you can employ the application director to search and launch the GUI utility.
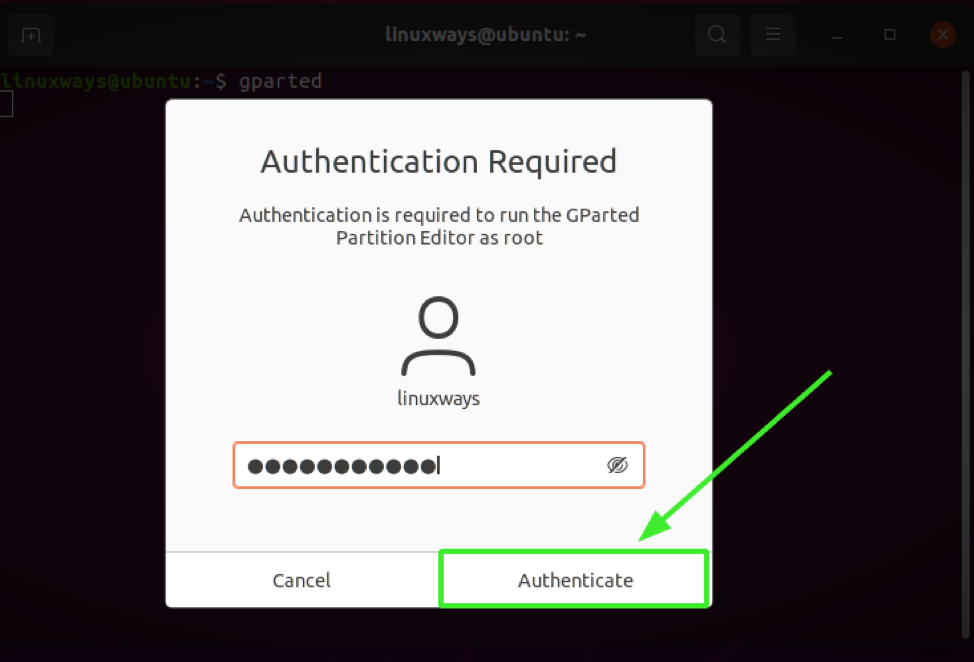
Provide your password to cosign and striking "ENTER".
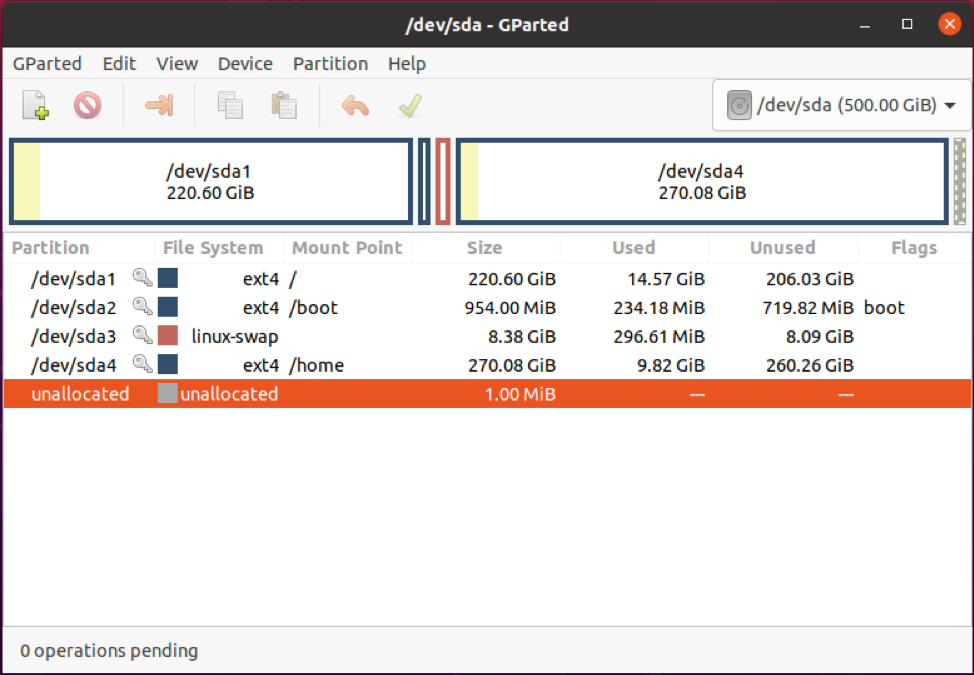
Once authenticated, Gparted will present the partitions on the principal difficult drive on which Linux is installed, in my case, information technology's /dev/sda.
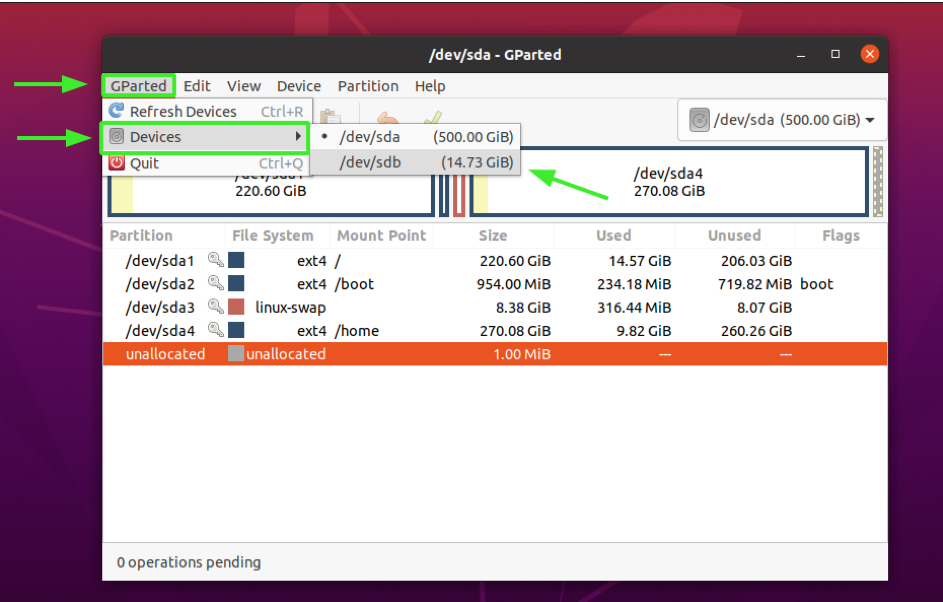
Since the division to be deleted is located on the removable drive, which is not listed, we will switch to that difficult bulldoze.
To do so, we volition go to Gparted > Devices > /dev/sdb
We now have the partitions of the second hard bulldoze listed, as shown below:
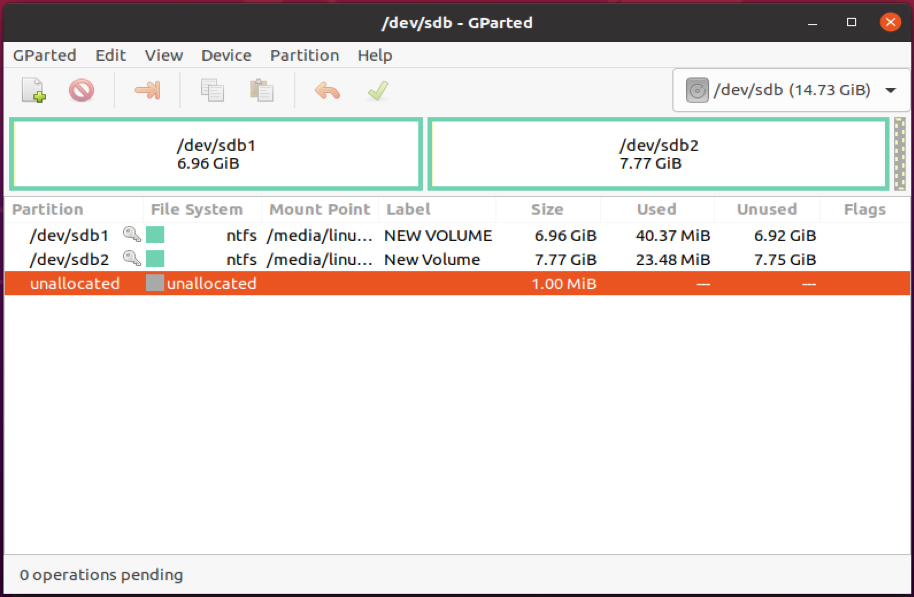
To delete the second partition (/dev/sdb2), we will unmount it first. And so, right-click and select "unmount".
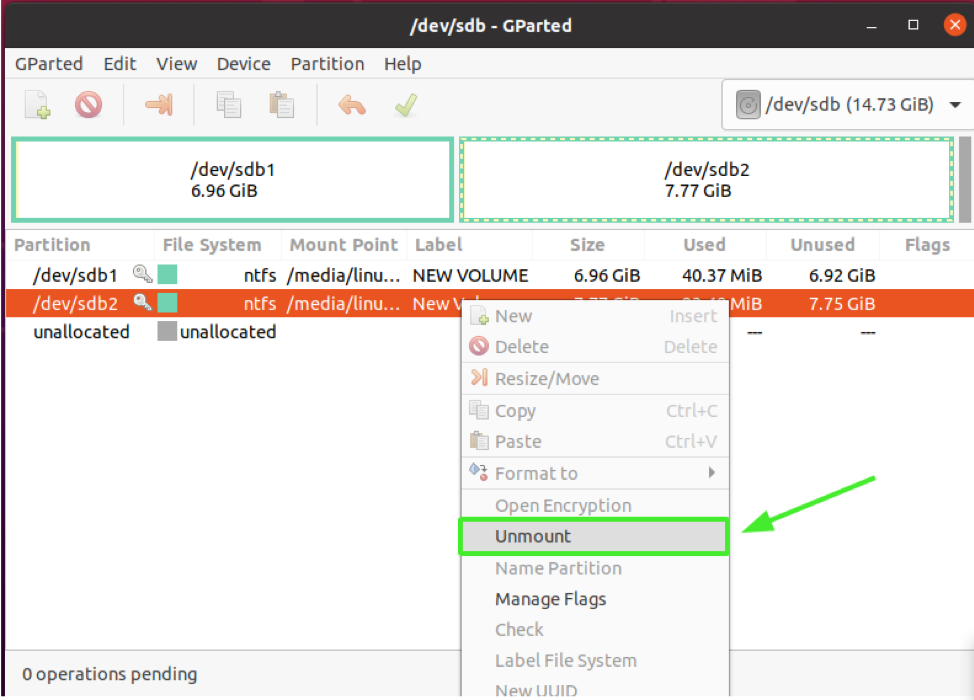
Next, right-click on the /dev/sdb2 sectionalization, and select the "delete" selection, which ultimately removes or deletes the partition.

Immediately, you volition realize that the partition is labeled "Unallocated" and at the bottom left corner of the Gparted window, you volition notice an alert informing yous of a pending operation. The reason you are getting this is that we have not saved the changes to the disk.
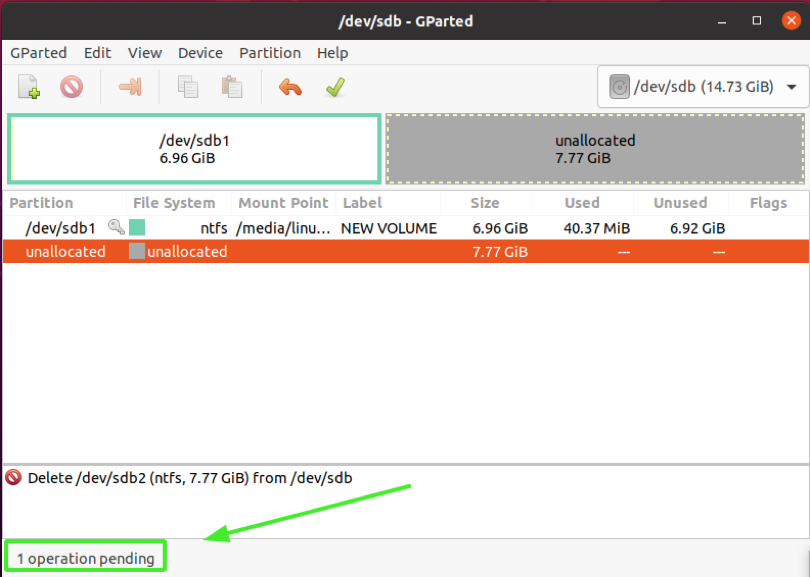
Click on the checkmark, every bit indicated, to utilize the changes made.

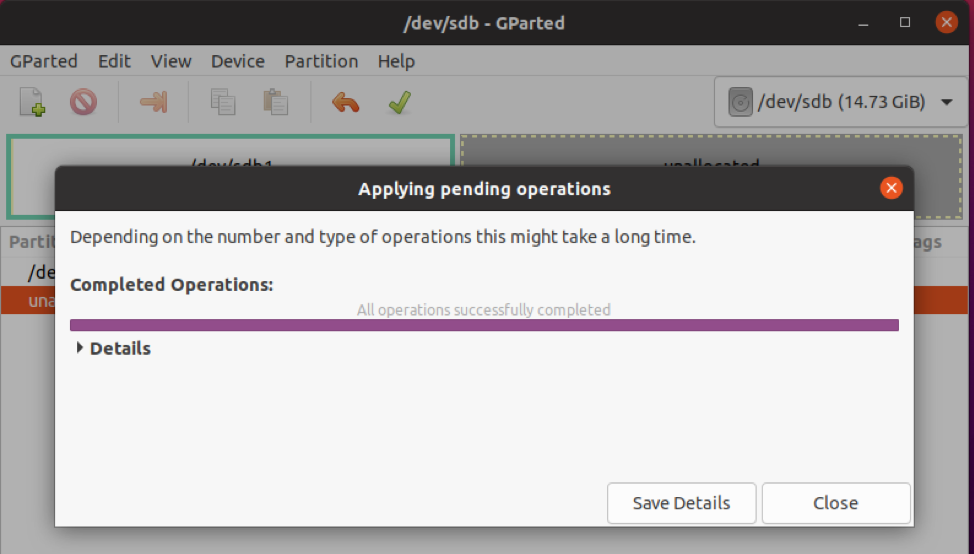
When prompted whether to proceed with the pending operations, click on "Apply".
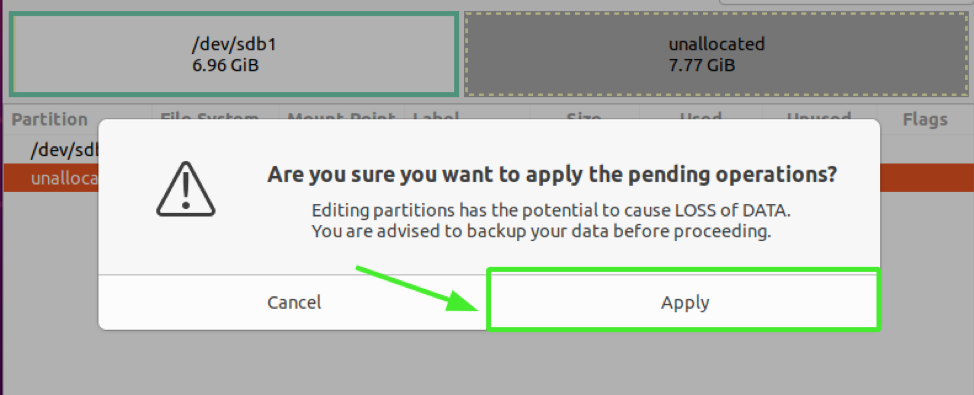
Ultimately, the writing process will conclude and the changes saved. Click on the "close" button.
Decision
We have covered two ways that yous tin employ to delete a logical partition in Linux: fdisk utility and Gparted GUI tool. If you find this informative, send u.s.a. a similar and share this guide.
cannadythersenight.blogspot.com
Source: https://linuxhint.com/delete-a-partition-in-linux/
0 Response to "How Delete All Partitions and Format It Again in Linux in Command"
Post a Comment